Apple Child Safety photo scanning — how it works and why it's controversial
Apple Child Safe photograph scanning — how it works and why it'south controversial

The newly announced Apple child condom toolset — which will scan iOS devices for images of child abuse — has rapidly become the subject of intense debate. While nobody can argue against protecting children from potential online abuse and harm, Apple's method brings upward questions of privacy and whether it may utilize this technology for other purposes in the hereafter.
With the update to the next generation of Apple OSes, U.S. users volition be subject to the new scanning system that comes as part of a wider set of tools designed to tackle child sexual assault textile (CSAM). If you're curious how the system functions, why some people are criticizing information technology and what it ways for your iPhone, we've explained what's going on beneath.
- iOS 15 release appointment, beta, supported devices and all the new iPhone features
- MacBook Pro 2021: Why I'm finally replacing my half dozen-year-former MacBook Pro
- Plus: Windows 11 on a Mac? Parallels 17 makes it possible
Apple tree Kid Safety photo scanning: how does it work?
As Apple tree writes in its introductory blog post, information technology's introducing several measures in iOS 15, iPadOS 15 and macOS Monterey "to protect children from predators who use communication tools to recruit and exploit them". The new versions of iOS, iPadOS and macOS are expected to leave beta this fall.
Apple's chief new tool is to check image hashes, a common method of examining images for CSAM. All digital images can be expressed as a "hash," a unique series of numbers that can be used to find identical images. Using a fix of CSAM hashes kept by the National Center for Missing and Exploited Children (NCMEC), Apple tree tin compare the hashes and see if any images on the device friction match.
This process all takes place on the device, with none of the user'due south local data existence sent elsewhere. Apple's system can too monitor your iCloud photo library for potentially offending material, but does this by checking images prior to upload, non past scanning the online files.
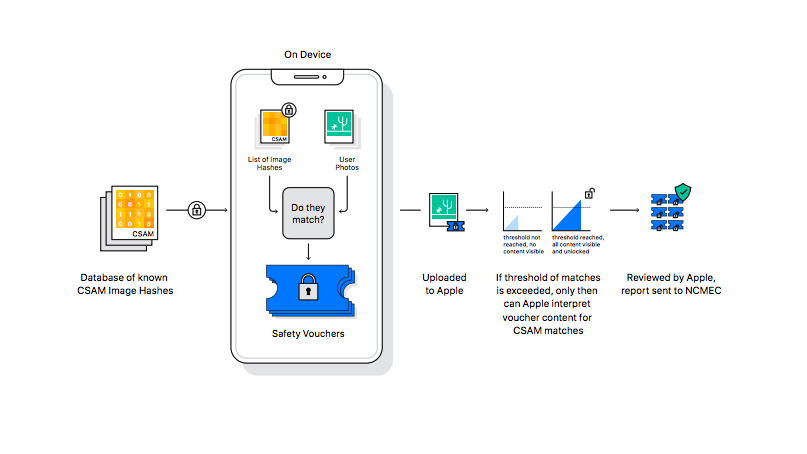
If Apple'due south system finds an image that matches with a CSAM hash, information technology will flag the photo. An account that accumulates multiple flags will then have the potential matches manually reviewed. If the image is decided to be genuine CSAM, Apple will close the account and notify the NCMEC. This may and then lead to a response by police force enforcement or legal action.
Users are able to appeal if they feel there's been an error. Nevertheless Apple tree is confident that the system won't give false positives. It gives a "less than a one in 1 trillion chance per year" of an business relationship beingness incorrectly flagged.
Since its initial announcement, Apple tree has further antiseptic its photograph-scanning policy. Apple now says that its scanner volition but hunt for CSAM images flagged by clearinghouses in multiple countries. The company also added that it would take 30 matched CSAM images earlier the system prompts Apple for a human review.
Apple Kid Rubber photo scanning: what else is involved?
Likewise equally the photo scanning system, Apple tree is introducing additional measures that can be enabled for child accounts in a user's family of devices. In the Messages app, whatsoever images the device believes could exist harmful — whether they're being sent or received — will be blurred out, and tapping it will display a pop-upwardly warning.
The warning states that the image or video may potentially be sensitive, and could take been sent to harm them, or purely by accident. It then gives the choice to dorsum out or to view the image. If someone opts to view the prototype, a subsequent screen explains that Apple will transport a notification to the kid'southward parents. Only after selecting to view the prototype a 2nd time volition the user be able to meet what was sent.
Siri is also being equipped with special answers to CSAM-related queries. It will either direct users to report suspected abuse or to seek assist depending on what is asked.
Apple Child Safety photo scanning: how will it bear on my Apple devices?
When upgrading to iOS 15, iPadOS 15 or macOS Monterey, you volition notice no deviation on your device or in your iCloud library when Child Safety is rolled out, unless you actually take CSAM or related data on them. The additional measures for child accounts will only be activated on accounts marked as such.
Too, there will exist no changes for Apple device users outside of the U.Southward. Nevertheless, information technology seems very likely that Apple will gyre out this organisation in other countries in future.
Apple Kid Safety photograph scanning: why are people criticizing information technology?
You lot may accept seen some heated criticism of Apple's new measures online. Information technology'south important to go on in listen that none of the individuals making these arguments are downplaying the importance of combating kid abuse. Instead, their main concerns are how this endeavour is counterbalanced against user privacy, and how this organisation could be altered in time to come for less noble ends.
There'southward also some anger at an apparent u-turn by Apple on user privacy. While other companies have been examining the contents of their products for years, Apple has been a notable exception to providing so-called "dorsum doors" in its devices, famously refusing the FBI access to a terrorism suspect's device in 2015. It also made a large step when it introduced App Tracking Transparency earlier this year, which lets users come across what data apps request, and block them from accessing it.
Apple says that considering the analysis and hashes are kept entirely on a user'southward device, the device remains secure even when checked for CSAM. However, as online privacy nonprofit Electronic Borderland Foundation argued in a contempo post, "a thoroughly documented, carefully thought-out, and narrowly-scoped backstairs is still a backdoor."
While the technology is exclusively focused on detecting CSAM, the ability to compare paradigm hashes on a device with an external database could theoretically exist adapted to check for other material. One example that'south frequently brought upwardly by critics would be governments targeting their opponents past creating a database of disquisitional material and so legally forcing Apple to monitor devices for matches. On a smaller scale, it's possible that entirely innocent images could be "injected" with lawmaking from offending ones, assuasive malicious groups to entrap or smear targeted people without them realizing before information technology's too late.
Matthew Green, acquaintance professor of information science at the John Hopkins Data Security Institute, wrote in a Twitter thread that checking photos on a user's device is much improve than doing so on a server. However he still dislikes Apple's system every bit it creates a precedent that scanning users' phones without consent is acceptable, which may lead to corruption from institutions who want to surveil iPhone users without due crusade.
Some experts advocate instead for more robust reporting tools to keep user privacy intact while notwithstanding ensuring details of CSAM are passed to the relevant authorities. Will Cathcart, caput of messaging service Whatsapp described Apple tree's plan as an overreach, and said Whatsapp, which has too been a strong advocate of end-to-end encryption, would non adopt a similar system, but rely on making user reporting as straightforward as possible.
In a certificate responding to often asked questions on the thing, Apple tree says it's incommunicable to utilize the existing system to observe hashes for annihilation beyond what the NCMEC has on its database due to the mode information technology was designed. It also says information technology would turn down any government requests to detect annihilation else. As for the injection question, Apple tree says that this isn't a risk since images are reviewed by humans before whatever potential action is taken.
Information technology's too early on to draw meaningful conclusions for now though, particularly since Apple tree is merely enabling the characteristic in the United States to beginning. Experts will exist standing to examine the verbal implementation of these tools, and so no dubiety this debate is going to go along for some time, and will take on new regional elements as Apple introduces these tools to more markets.
Source: https://www.tomsguide.com/news/apple-child-safety-photo-scanning-how-it-works-and-why-its-controversial
Posted by: wolfbrejack.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Apple Child Safety photo scanning — how it works and why it's controversial"
Post a Comment